Comprehensive Guide to Chronic Disease Management: Diabetes and Hypertension
Chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension (high blood pressure) are prevalent and require careful management to prevent complications and improve quality of life. This guide explores effective strategies for managing these conditions, focusing on how to handle them together, and provides insight into chronic care management, treatment options, and guidelines.
Understanding Diabetes and Hypertension
Diabetes
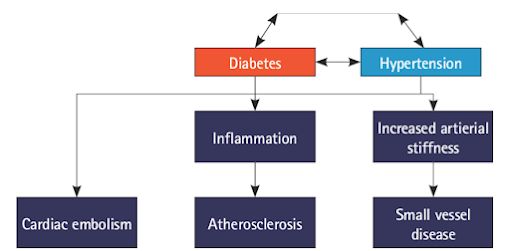
Diabetes is a condition where the body either cannot produce insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or cannot use insulin effectively (Type 2 diabetes). Insulin is crucial for converting glucose from food into energy. Without proper management, diabetes can lead to various complications, including cardiovascular issues, nerve damage, and kidney problems.
Hypertension
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, occurs when the force of blood against the artery walls is consistently too high. It can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. Often referred to as the “silent killer,” hypertension may not present symptoms until it has caused significant damage.
How to Manage Diabetes and Hypertension Together
Managing diabetes and hypertension simultaneously can be challenging but is essential for overall health. Here are key strategies:
Integrated Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle benefits both conditions. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reduce salt intake to manage blood pressure and monitor carbohydrate intake to control blood sugar levels.
Regular Physical Activity: Exercise helps lower blood pressure and improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week, such as brisk walking or cycling. Include strength training exercises twice a week to enhance overall fitness.
Routine Monitoring: Keep track of your blood pressure and blood glucose levels regularly. This helps in adjusting treatments and managing both conditions effectively. Use home monitoring devices and attend regular check-ups with your healthcare provider.
Medication Management: Many individuals with diabetes and hypertension require medication. Ensure that you understand how each medication works and its potential side effects. Regularly review your medications with your healthcare provider to avoid drug interactions and optimize your treatment plan.
Stress Management: Stress can negatively impact both blood sugar and blood pressure levels. Incorporate stress-reducing practices into your routine, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in hobbies you enjoy.
Education and Support: Educate yourself about both conditions and seek support from healthcare professionals, diabetes educators, and support groups. Knowledge and support are crucial for managing chronic diseases effectively.
What is Chronic Care Management for Hypertension?
Chronic care management for hypertension involves a structured approach to managing high blood pressure over the long term. This includes:
Personalized Treatment Plans: Creating a tailored treatment plan based on individual health needs, risk factors, and lifestyle. This may include lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring.
Regular Follow-Ups: Scheduling routine appointments with healthcare providers to monitor blood pressure and adjust treatment as necessary. Regular follow-ups ensure that any changes in blood pressure or health status are addressed promptly.
Patient Education: Providing patients with information about managing hypertension, including dietary recommendations, the importance of medication adherence, and recognizing symptoms that require medical attention.
Collaborative Care: Involving a team of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, dietitians, and pharmacists, to provide comprehensive care and support.
Self-Management Support: Encouraging patients to actively participate in their care by monitoring their blood pressure, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and understanding their condition.
What is the First Line of Treatment for Hypertension in Diabetic Patients?
For patients with both diabetes and hypertension, the first line of treatment often includes:
ACE Inhibitors or ARBs: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are commonly prescribed. These medications help lower blood pressure and provide kidney protection, which is particularly important for diabetic patients.
Lifestyle Modifications: Alongside medication, lifestyle changes play a crucial role. Emphasize a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, and weight management to control both blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
Monitoring and Adjustments: Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood glucose levels is essential. Based on these measurements, healthcare providers may adjust medications to achieve optimal control of both conditions.
What are the Guidelines for Hypertension for Diabetic Patients?
Guidelines for managing hypertension in diabetic patients generally include:
Blood Pressure Targets: Aim for a blood pressure target of less than 130/80 mmHg, as recommended by various health organizations. This target helps reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications and kidney damage.
Medication Recommendations: Use medications such as ACE inhibitors or ARBs as first-line treatments. Other antihypertensive medications may be added based on individual patient needs and responses.
Regular Screening: Regular screening for hypertension and diabetes complications is crucial. This includes monitoring kidney function, eye health, and cardiovascular health.
Comprehensive Management: Address all aspects of health, including blood glucose control, cholesterol levels, and lifestyle factors. A holistic approach helps improve overall outcomes and quality of life.
Conclusion
Managing chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension requires a multifaceted approach. By integrating lifestyle changes, medication management, regular monitoring, and patient education, individuals can effectively manage both conditions and reduce the risk of complications. Remember, working closely with healthcare providers and staying informed about your conditions is key to achieving optimal health.
For personalized advice and treatment plans, consult with your healthcare provider. They can offer guidance tailored to your specific needs and help you navigate the complexities of managing chronic diseases.
Comments
Post a Comment